
Atomic size is defined in several different ways and these different definitions often produce some variations in the measurement of atomic sizes.īecause it is so difficult to measure atomic size from the nucleus to the outermost edge of the electron cloud, chemists use other approaches to get consistent measurements of atomic sizes. The region in space occupied by the electron cloud of an atom is often thought of as a probability distribution of the electrons and therefore, there is no well-defined "outer edge" of the electron cloud.
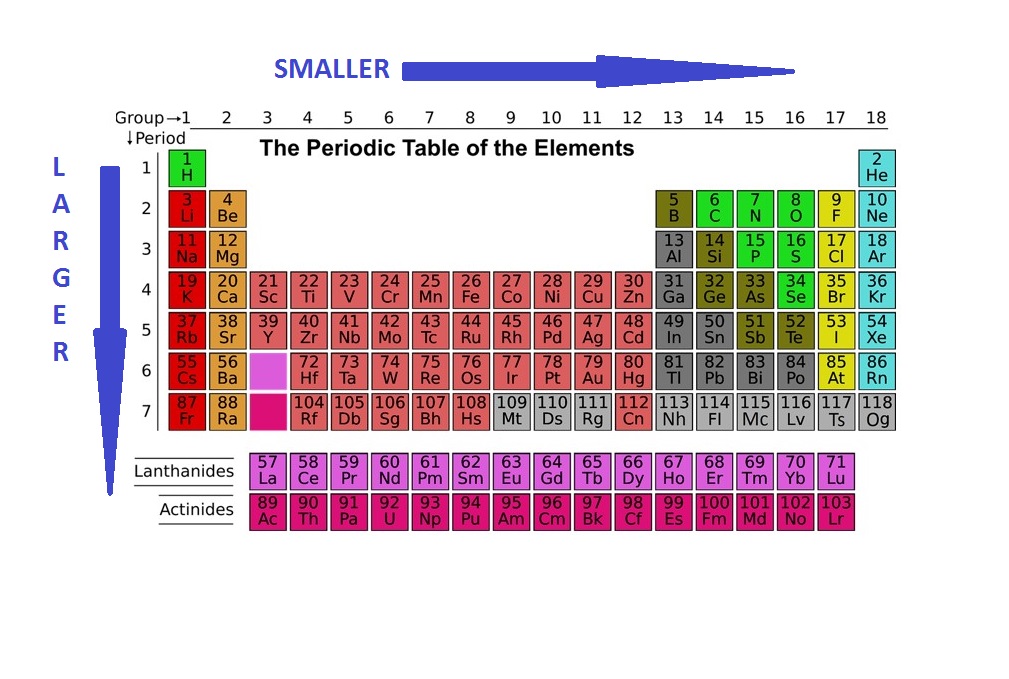
Use the concept of effective nuclear charge to explain why the atomic radii of the main group elements increase when we move down a group in the periodic tableĪtoms Have No Definite Boundary. Use the general trends to predict the relative sizes of atoms. Describe how the trend of atomic radii works for transition metals. Describe the trend of atomic radii in the rows in the Periodic Table. Describe the general trend in atomic size for groups and for periods. Describe the factors that determine the trend of atomic size. Describe measurement methods for atomic size. State the boundary issue with atomic size. The number of electrons held between the nucleus and its outermost electrons (called the shielding effect). The number of energy levels holding electrons (and the number of electrons in the outer energy level). The number of protons in the nucleus (called the nuclear charge). The actual trends that are observed with atomic size have to do with three factors. Each of these trends can be understood in terms of the electron configuration of the atoms. The two following this lesson will discuss ionization energy and electron affinity. The first lesson of this chapter is devoted to the trend in atomic size in the Periodic Table. There are three specific periodic trends that we will discuss. This means is that as you move down a group or across a period, you will see a trend-like variation in the properties. In the Periodic Table, there are a number of physical properties that are not really "similar" as it was previously defined, but are more trend-like. 5 For the Transition Elements, the Trend is Less Systematic. 4 Atomic Size in a Period Decreases from Left to Right. 3 Atomic Size in a Column Increases from Top to Bottom. Smallest and Largest Atomic Radiusįrancium has the largest atomic size on the periodic table, and helium has the smallest atomic size. The Trend on a GraphĪs shown in the graph below, the atomic radius is largest at the first element in each period, and it decreases down each period. As electron cloud sizes increase, so do atomic radii. This is because between each group, electrons occupy successively higher energy levels. Group Trendĭown a group, atomic radii increase. 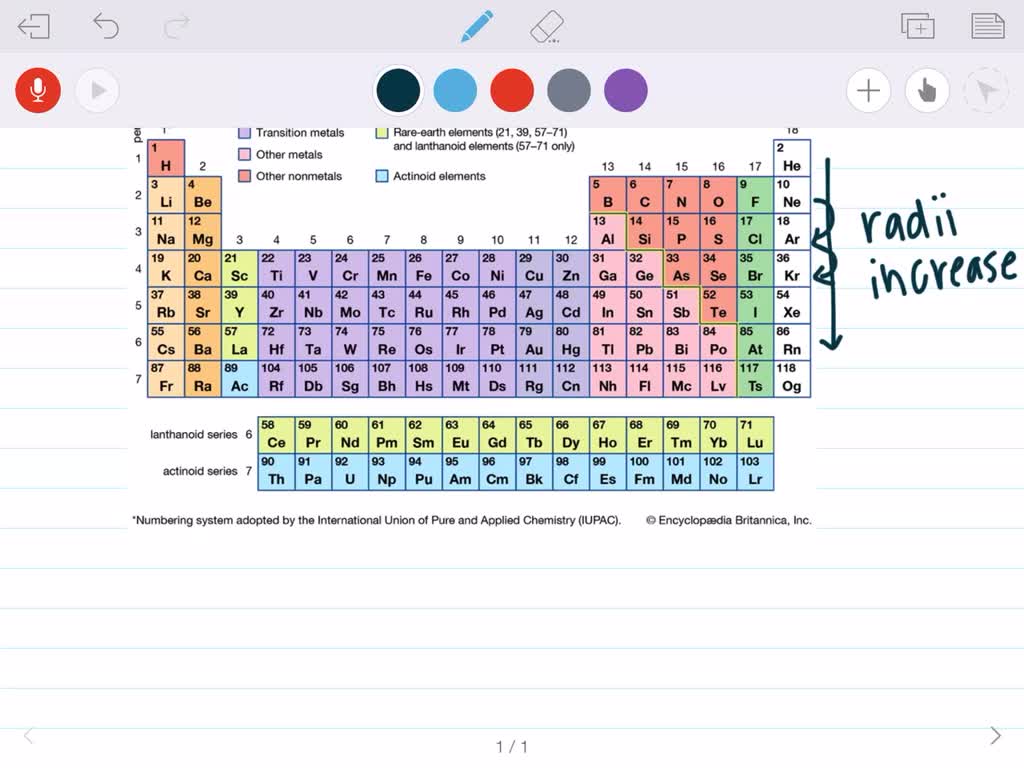
This is why the difference in atomic radii decreases down each period. One thing to note is that the effect of the attraction between the positively charged nucleus and the electrons is slightly countered by the repulsion of electrons as they are successively added. This increased positive charge attracts or pulls, the electrons in closer to the nucleus, decreasing the atomic radius. Down the period, however, the number of protons also increases. This is because while the number of electrons increases down the period, they only add to the same main energy level, and therefore do not expand the electron cloud.

For example, ionization energy, electronegativity, and of course atomic radius which we will discuss now. There are many trends on the periodic table. Let’s break down the trend into its period and group trends.

Atoms decrease in size across the period and increase in size down the group. Atomic Radius Trend on the Periodic TableĪtomic radii increase toward the bottom left corner of the periodic table, with Francium having the largest atomic radius. Thus the atomic radius is measured as shown in the diagram below. This is because the borders of orbitals are quite fuzzy, and they also change under different conditions. While your initial thought may have been to measure the distance from the center of an atom’s nucleus to the edge of its electron cloud, this is inaccurate and not feasible. The atomic radius is measured as half the distance between two nuclei of the same atoms that are bonded together. Let’s discuss the definition of the atomic radius, also called atomic size, and the atomic radius trend on the periodic table.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
